Landing cost is a crucial concept in international trade, representing the total cost of a product once it has arrived at a buyer’s doorstep. It includes the original price of the product, transportation fees, customs duties, taxes, insurance, currency conversion, and other costs associated with bringing a product from the seller to the buyer. Understanding and accurately calculating landing costs is essential for businesses to determine the true cost of imported goods, set appropriate pricing strategies, and maintain profitability.
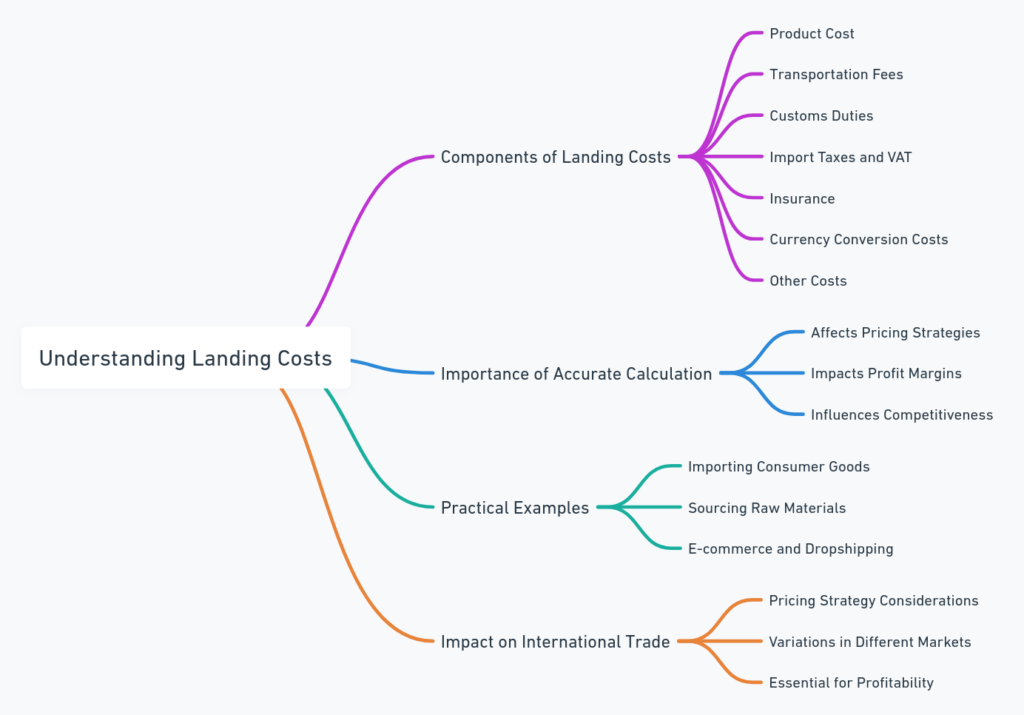
Understanding Landing Costs
- Components of Landing Costs:
- Landing costs include various expenses incurred in the process of purchasing and importing goods. Key components typically include:
- Product Cost: The original purchase price of the goods.
- Transportation Fees: Costs associated with shipping the goods from the seller to the buyer, including freight and logistics fees.
- Customs Duties: Taxes imposed by the importing country on imported goods.
- Import Taxes and VAT: Additional taxes that may be levied by the importing country, such as value-added tax (VAT).
- Insurance: Costs for insuring the goods during transportation.
- Currency Conversion Costs: Costs associated with converting payment from one currency to another.
- Other Costs: Additional costs such as handling fees, storage fees, and agent fees.
- Landing costs include various expenses incurred in the process of purchasing and importing goods. Key components typically include:
- Importance of Accurate Calculation:
- Accurately calculating landing costs is vital for businesses to understand the true cost of their imported goods. It affects pricing strategies, profit margins, and competitiveness in the market.
- Example: A retailer importing electronics from China needs to calculate the landing cost to determine the final selling price and ensure profitability.
- Impact on Pricing Strategy:
- Landing costs directly impact how businesses price their products. Underestimating these costs can lead to reduced profit margins, while overestimating can result in uncompetitive pricing.
- Example: A furniture importer includes all landing costs in its pricing strategy to remain competitive while ensuring a healthy profit margin.
- Considerations for Different Markets:
- Landing costs can vary significantly depending on the destination market due to differences in customs duties, taxes, and transportation costs.
- Example: An apparel company finds that landing costs are higher when importing into the European Union compared to the United States, due to different duty rates and tax structures.
Practical Examples of Landing Costs
- Importing Consumer Goods:
- A business importing consumer goods, such as clothing or electronics, must consider factors like freight charges, insurance, customs duties, and VAT when calculating the landing cost.
- Example: An electronics dealer importing smartphones from South Korea calculates the landing cost to include freight, insurance, customs duties, and VAT to determine the final cost per unit.
- Sourcing Raw Materials:
- Manufacturers sourcing raw materials from abroad need to factor in landing costs to determine the total cost of production.
- Example: A car manufacturer importing steel from Japan calculates the landing cost, including transportation and duties, to assess the overall production cost of vehicles.
- E-commerce and Dropshipping:
- E-commerce businesses and dropshippers must consider landing costs, especially when sourcing products from international suppliers, to set accurate prices and maintain profit margins.
- Example: An online store dropshipping fashion accessories from China includes all associated landing costs in its pricing model to ensure profitability.
Importance of Landing Costs
Landing costs play a critical role in international trade, affecting businesses’ pricing strategies, profitability, and competitiveness. Accurate calculation of these costs is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, setting appropriate prices, and maintaining healthy profit margins. Businesses engaged in importing goods must have a clear understanding of all components of landing costs to succeed in the global market.
In conclusion, landing cost is a vital concept in international trade, encompassing all costs associated with bringing a product from the seller to the buyer. Accurate calculation of landing costs is crucial for businesses to determine the true cost of imported goods, set appropriate pricing, and maintain profitability. Understanding and effectively managing these costs is key to success in the global marketplace.
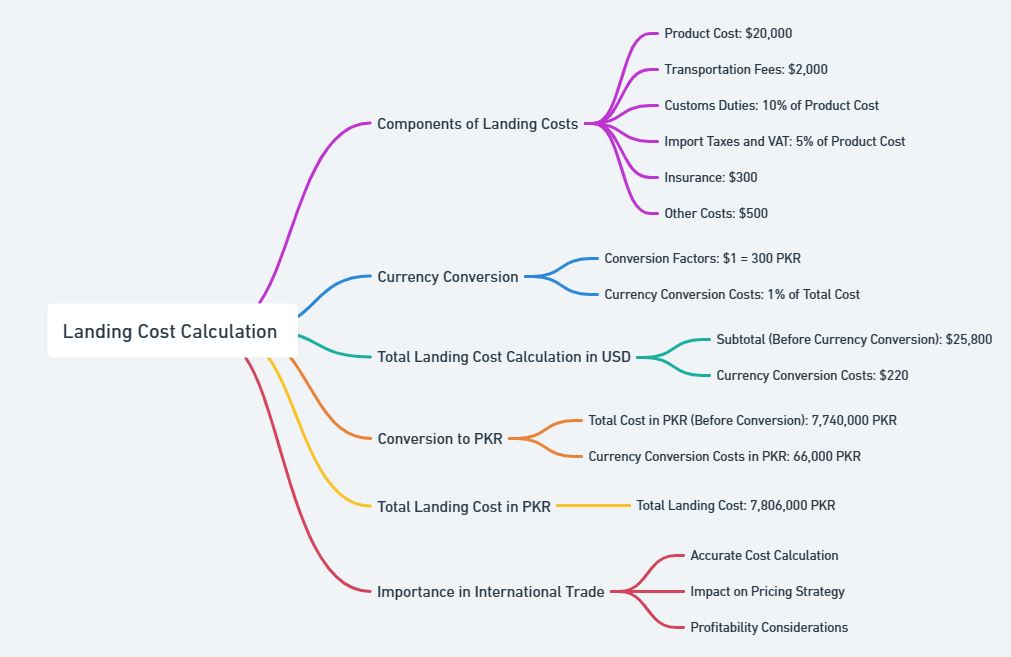
Hypothetical Example: Importing Electronic Goods from China to Pakistan
Let’s consider a hypothetical example of a business importing electronic goods from China to Pakistan. We’ll go through a small numerical calculation to determine the landing cost of the imported goods.
Assumptions:
- Product Cost (Cost of Goods): $20,000
- Transportation Fees (Freight Charges): $2,000
- Customs Duties: 10% of the product cost
- Import Taxes and VAT: 5% of the product cost
- Insurance: $300
- Currency Conversion Costs: 1% of the total cost (product cost + transportation fees)
- Other Costs (Handling, Storage, etc.): $500
- Conversion Factors: $1 = 300 PKR
Calculation in USD:
- Product Cost: $20,000
- Transportation Fees: $2,000
- Customs Duties: 10% of $20,000 = $2,000
- Import Taxes and VAT: 5% of $20,000 = $1,000
- Insurance: $300
- Other Costs: $500
- Subtotal (Before Currency Conversion): $20,000 + $2,000 + $2,000 + $1,000 + $300 + $500 = $25,800
- Currency Conversion Costs: 1% of ($20,000 + $2,000) = $220
Conversion to PKR:
- Total Cost in USD (Before Currency Conversion): $25,800
- Total Cost in PKR (Before Currency Conversion): $25,800 * 300 PKR = 7,740,000 PKR
- Currency Conversion Costs in PKR: $220 * 300 PKR = 66,000 PKR
Total Landing Cost Calculation in PKR:
- Total Landing Cost in PKR: 7,740,000 PKR + 66,000 PKR = 7,806,000 PKR
Conclusion:
The total landing cost for importing the electronic goods from China to Pakistan, when converted to Pakistani Rupees, is approximately 7,806,000 PKR. This calculation includes the costs of the goods, transportation, customs duties, taxes, insurance, currency conversion, and other associated costs, all converted to the local currency at the specified exchange rate.
This example demonstrates the importance of considering currency conversion when calculating the total landing cost for imported goods, especially in international trade scenarios involving different currencies.

